Texas Tenant-Landlord Law
Fair Housing
The Fair Housing Act was created in order to ensure that everyone is treated equally during the housing process. It protects tenants from discrimination when searching for a rental property. At the federal level the Fair Housing Act protects the following classes:
- Race
- Color
- National Origin
- Religion
- Sex
- Familial Status
- Disability
Learn about fair housing at the federal level here.
In addition to federal housing laws, the Texas Fair Housing Act (1993) protects your right to rent an apartment, buy a home, obtain a mortgage, or purchase homeowners insurance free from discrimination. Learn more about the Texas Fair Housing Act here.
Some cities, counties, and other municipalities may have additional housing discrimination laws to protect additional groups. To find out about existing additional protections in your City, County, or municipality, find website listings in the Texas.gov directory or find and contact your local Legal Aid Office using TXLawHelp.org.
Security Deposits
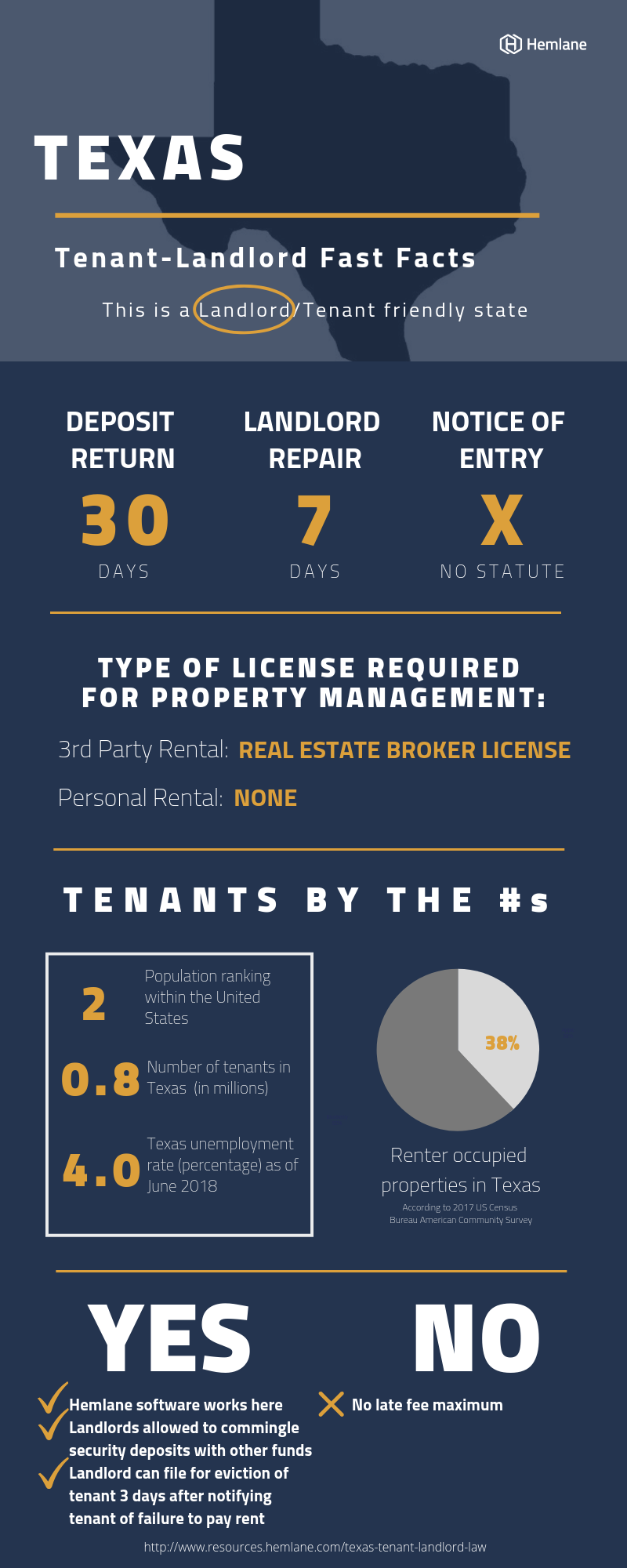
- In Texas, it is not required for a landlord to ask for a security deposit and has no limit on how much they can ask for. But, security deposits prove a tenant’s financial stability and provide collateral for the landlord if property damage compensation were to be required, so it is a smart idea to issue one.
- Landlords aren’t restricted from combining security deposits with other assets and are also not mandated to pay interest on such accounts if commingled.
- Once the lease is up, the landlord must return the full amount back to the tenant within 30 days, unless substantial damages have been incurred.
- If they have, the landlord is mandated to issue an itemized list of repairs and their costs to the tenant within 30 days of moving-out. (92.104) Normal wear and tear should be not considered in damage costs.
- Tenants are also allowed to issue a Notice of Surrender in order to receive their security deposit back sooner than 30 days. This ability must be clearly allowed and stated in the lease agreement, however.
Rent and Late fees
- A late fee isn’t required in Texas, but if one is issued, it shouldn’t amount to more than the costs that a landlord would face as a result of the late payment, and the ability to do so must be stated clearly in the lease agreement. (§92.109)
- In Texas, there is a legal grace period of 1 day for the tenant to turn in rent. After this day has passed, the landlord is legally allowed to consider the tenant to be violating the lease and collect a late fee. If rent is still unpaid, the landlord must wait three days before giving the tenant a pay or quit notice.
Notice and Entry
- In Texas, the landlord is required to give notice prior to entering the property, but there is no statute on the specified period. (92.0081)
- There are also no statutes on when a landlord is required to notify a tenant regarding emergency entry or extended absence.
- In order to terminate a yearly lease early, the landlord must notify the tenant at least one month in advance
- In order to terminate a month-to-month lease early, the landlord must also notify the tenant at least one month in advance, but can make written agreements stating differently when signing the lease
- If the tenant wishes to terminate the lease early, they have to give a notice period of 10 days for a week to week tenancy; 30 days for a month to month tenancy; until the end of the lease for an annual lease.
- In order to terminate a month-to-month lease early, the landlord must also notify the tenant at least one month in advance, but can make written agreements stating differently when signing the lease
Disclosures
- In Texas, a landlord is allowed to remove personal property from a deceased tenant, if the person-of-contact has not claimed the items 30 days after notice. (Sec. 92.014.5)
- Landlord must inform the tenant, in writing, that they have the right to “Repair and deduct or the option to terminate the lease,” if the Landlord fails to make repairs that directly affect the health or safety of an ordinary tenant
- Federal law requires landlords to disclose known information on lead-based paint and lead-based paint hazards before the lease takes effect. Additionally, under state law, landlords must provide this EPA-approved information pamphlet and fill out the following form.
- If utilities are provided by a landlord and stated in the lease, and the tenant receives a notice from the service that they are about to be shut off, the landlord is liable.
- Landlords can require tenants to provide proof of domestic violence status before releasing tenants from a lease.
Texas Eviction Laws

- When it is failure to pay rent, the tenant has 3 days to pay you otherwise the eviction notice can be filed with the courts.
- When there is another lease violation (e.g. subletting), there is no no statute the tenant has to follow reagrding time given to resolve the violation from the point that the eviction notice is served. Otherwise the eviction notice will be filed with the courts.
As the situation with COVID-19 continues to evolve, the moratorium on foreclosures and evictions will continue to impact millions of rental properties across the country. For the most up to date information on this legislation, as well as to see if your city or county has additional directives in place, please contact your local representative.




